Panjab University gets patent for technology to biodegrade pesticide malathion
PU scientists develop eco-friendly solution for pesticide pollution

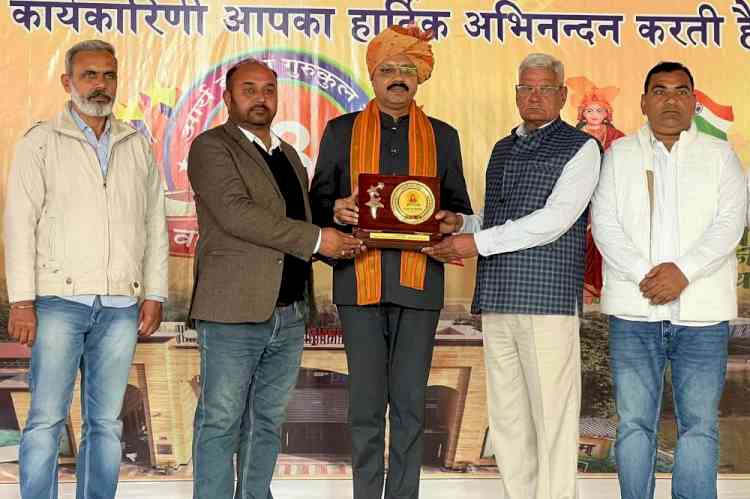
Chandigarh, December 2, 2025: Panjab University(PU), Chandigarh has received a patent for a new biodegradation technology that offers a safe and effective way to break down the harmful pesticide malathion. The invention has been developed by Dr Deepak Kumar Rahi from the Department of Microbiology and Dr Aruna Singh Parmar, his former PhD scholar and co-inventor.
The patented work is titled Immobilised Fungal Enzyme for Use as Biodegrading Agent of Organophosphorus Insecticide (Malathion). This is the first scientific report of malathion degradation using an immobilised fungal cutinase enzyme. The method provides a sustainable alternative to chemical or physical clean-up techniques.
The enzyme converts malathion, widely used in farming, into harmless and non-toxic metabolites. University officials said the technology could help lower toxic residues in soil, crops and water bodies. It may also reduce risks linked to human exposure and support safer farming practices by restoring soil quality.
The process uses fungal cutinase from Fusarium verticillioides MTCC 13376. The enzyme is immobilised on amino-functionalised magnetic nanoparticles. These increase in size from 24.5 nanometres to 74 nanometres after enzyme binding, showing efficient immobilisation. The enzyme kept 60 per cent activity after six reuse cycles and 70 per cent activity after 30 days of storage. The nanoparticles show strong thermal stability and spherical uniformity. All degradation products are reported to be non-toxic.
The technology could be used in agriculture, wastewater treatment, food safety and larger environmental clean-up tasks. It has potential for scale-up and industrial use due to its stability and reusability.


 City Air News
City Air News 










