Dhemaji 2004 blast case: Himanta asks DGP to study court's verdict
A day after the Gauhati High Court acquitted all accused in the 2004 Dhemaji bomb blast case which claimed 18 lives, Chief Minister Himanta Biswa Sarma asked the Assam DGP G. P. Singh to study the verdict.
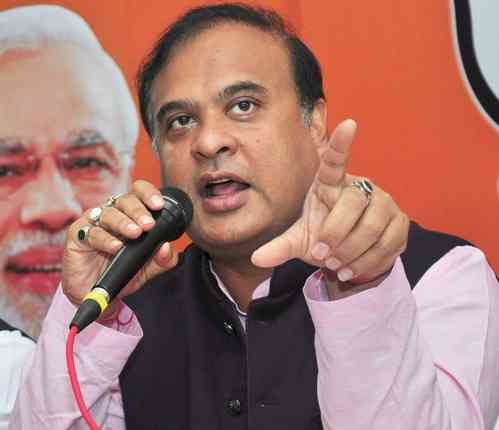

Guwahati, Aug 26 (IANS) A day after the Gauhati High Court acquitted all accused in the 2004 Dhemaji bomb blast case which claimed 18 lives, Chief Minister Himanta Biswa Sarma asked the Assam DGP G. P. Singh to study the verdict.
"I have asked the DGP to study the Gauhati High Court's ruling, and the state will take decision to appeal against the order only after thorough study of the verdict," Sarma told media persons on Friday evening.
"Let's understand the judges' reasoning for coming to this verdict. It wasn't until yesterday that a copy of the ruling became accessible,” he said.
The Gauhati High Court on Thursday overturned the 2019 verdict of the Dhemaji District and Sessions Court by acquitting all six accused in the 2004 Dhemaji bomb blast of all charges.
Six persons were found guilty by the lower court in July 2019 and four received life sentences, while two got four years of rigorous imprisonment.
The High court reversed the 2019 verdict of the lower court after observing that sufficient evidence against the accused had not been produced.
On August 15, 2004, a bomb exploded in Dhemaji town during the Independence Day celebrations, killing 18 people, including 14 schoolchildren, and critically injuring at least 40 others.
According to a top Assam police official, the explosion at Dhemaji College Playground at 8.55 a.m. and claimed the lives of children who were participating in celebrations for Independence Day.
Later, the banned militant outfit United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA) claimed responsibility for the attack, and within a short period of time, police arrested at least 14 people.
Police filed cases against them under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), section 120 B of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), which deals with criminal conspiracy, section 302 of the IPC, and other sections.


 IANS
IANS